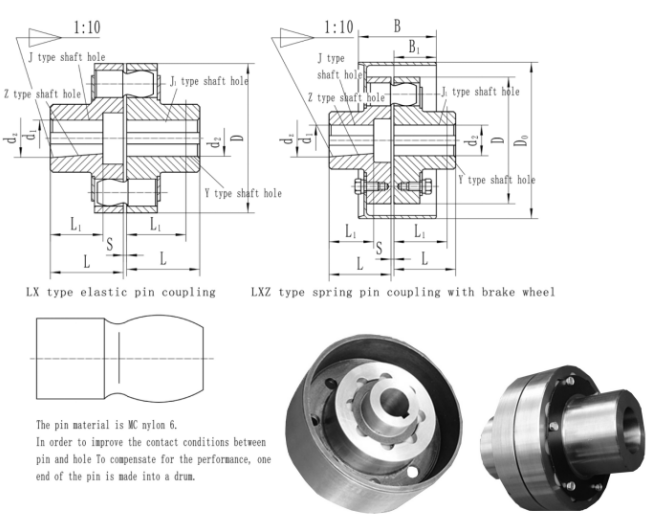
Elastic pin coupling
The elastic pin coupling is a pin made of several non-metallic elastic materials, which is placed in the flange hole of the two coupling halves. The coupling of the two coupling halves is realized by the pin. The coupling has a simple structure and is easy It is more convenient to manufacture, install, disassemble and replace the elastic element without moving the two couplings.
The material of the elastic element (column pin) is generally nylon 6. It has the ability to compensate for the offset of the two axes in a slight amount. The elastic element is sheared during operation, and the working reliability is extremely poor. It is suitable for working conditions with high reliability requirements. For example, the drive shaft system of the lifting mechanism of the lifting appliance must not be used. It is not suitable for low-speed load-bearing and high impact and vibration drive shaft systems. For radial and angular Drive shafts with large deviations and low installation accuracy should not be used. Elastic pin coupling The pin in the shaft is in a shear and squeeze state during operation. The strength condition is to calculate the shear strength of the elastic pin cross section and the squeeze strength of the pin and the pin hole wall.
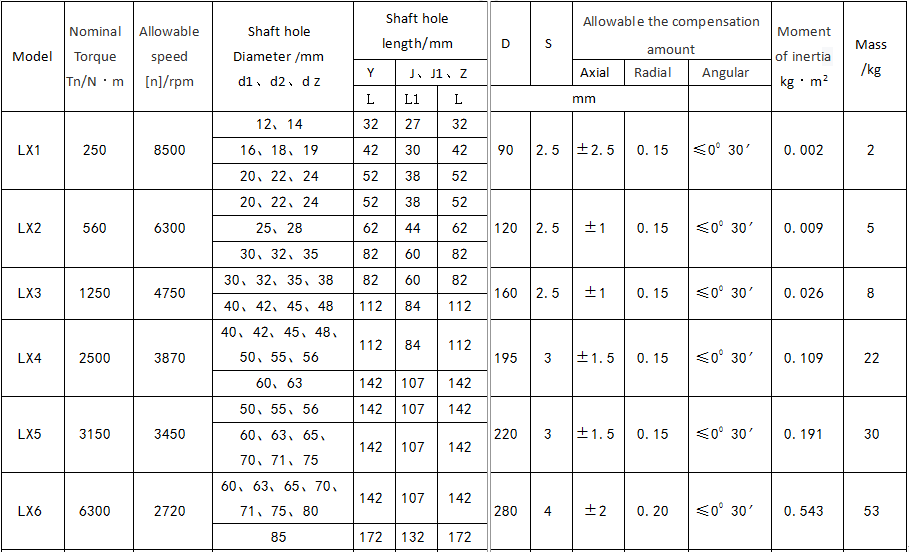
The elastic pin coupling (GB5014-85) is suitable for various coaxial transmission systems. The torque is transmitted by the shear strength of the nylon rod cross section. The nominal torque is 160-160000N.M, and the working temperature is -20℃- 80℃. The structure is simple, with cushioning and shock absorption performance and a certain axis offset compensation ability, suitable for use in environments where noise is not controlled. Allowable compensation amount Radial 0.15-0.25mm Angle 0.5°.
The shaft hole type is cylindrical (Y), conical (Z) and short cylindrical (J). The shaft hole and keyway are processed in accordance with the provisions of the national standard GB3852-83 "Coupling Shaft and Keyway Form and Size". The semi-coupling is made of precision casting, cast iron HT20-40, cast steel ZG35Ⅱ, shaft hole and keyway are drawn, and the pin is made of MC nylon b.
1. The stress of the elastic pin coupling: due to the difference in heating between the inside and outside of the metal, the expansion is uneven, resulting in internal stress, called thermal stress. If the temperature is too high during annealing to cause graphite cross-section, it will be difficult to cut and overheat and deform during quenching. Decarburization causes soft spots on the surface of the workpiece, reducing the surface hardness, wear resistance and fatigue strength.
2. Oxide skin of elastic pin coupling:
3. Hard and brittle mesh carbide of elastic pin coupling:
4. Decarbonization of the elastic pin coupling: Decarbonization refers to the phenomenon that all or part of the carbon on the steel surface is burned off.
5. Overheating and overburning of the elastic pin coupling: Overheating means that after the steel exceeds the allowable temperature during heating, the grains grow thicker.
Elastic pin couplings are generally elastic pin couplings and nylon rod pin couplings. The former is connected by several screws. The nut end of the screw is equipped with elastic washers. The latter is made of nylon rods, and the two half couplings are drilled with holes of the same size, inserted with nylon rods, and covered with a baffle outside. The pin coupling is simpler. It is the two half couplings. The sections are connected with N nylon rods. Can play a role in compensation.
Pin coupling, commonly used models are, elastic sleeve column coupling (LT), elastic column coupling (LX), elastic pin gear coupling (LZ).
The basic parameters of the LZ elastic pin gear coupling and the pins mainly made of several non-metallic materials are placed in the coupling holes between the two coupling halves and the inner surface of the outer ring, and the rotation is transmitted through the pin Moment to realize the coupling of the two coupling halves.
LT type (formerly TL type) elastic sleeve pin coupling (GB4323-2002 instead of GB4323-1984) The elastic sleeve pin coupling is to use a pin with an elastic sleeve (rubber material) at one end, which is installed in the two halves of the coupling In the flange hole of the shaft, to realize the coupling of the two coupling halves. The elastic sleeve pin coupling was once the most widely used coupling in China. As early as the late 1950s, it was formulated as the standard of the Ministry of Machinery. JB08-60 elastic ring pin coupling is the first department in China. Standard coupling.
LX type-elastic pin coupling has been listed as national standard GB5014-85, suitable for various mechanical transmission shafts connecting two coaxial lines, usually used for frequent high and low speed movements. The working temperature is -20 ~ +80 ℃; the transfer nominal torque is 40 ~ 20000N.m. The elastic pin coupling has a large structure, simple and reasonable, easy maintenance, interchangeable symmetrical sides, long life, allowing large axial movement, with cushioning, shock absorption, wear resistance and other properties.
heating time
Heating of the elastic coupling forging will cause the workpiece to crack during heating, causing the workpiece to crack after turning and scrapped. If banded carbides appear on the surface of the elastic coupling, the hardness and structure after quenching and tempering will be uneven and easily deformed. This is also a defect in the banded structure of pearlite and ferrite along the processing deformation direction . However, if it is underheated or the temperature is low during annealing, the pearlite cannot complete globalization, which is also not conducive to cutting and subsequent heat treatment. There is no remedy for overburning. Failure to remove the oxide scale will affect the turning process. Overburning refers to the phenomenon that the metal appears to be oxidized or partially melted due to the heating time being too long and the temperature being too high.
1. Oxide scale: Oxide scale not only loses a lot of steel, but also reduces the surface quality of the forging and the service life of the forging die. If pressed into the metal, it will cause the forging to be scrapped.
2. Hard and brittle network carbides: It weakens the bonding force between the crystal materials, significantly deteriorates the mechanical properties, especially reduces the impact toughness, but can be improved or eliminated by normalizing.
3. Decarburization: Decarburization refers to the phenomenon that all or part of the carbon on the steel surface is burned off.
4. Overheating and overburning of the elastic pin coupling: Overheating means that the steel grows thicker after the steel exceeds the allowable temperature during heating.
5. Stress occurs: due to the difference in heating between the inside and outside of the metal, the expansion is uneven, and the internal stress is generated, which is called thermal stress. If the temperature is too high during annealing to cause graphite cross-section, it will be difficult to cut and overheat and deform during quenching. Decarburization causes soft spots on the surface of the workpiece, reducing the surface hardness, wear resistance and fatigue strength.
6. There is a fracture in the cross section of the elastic pin coupling: this defect destroys the chemical composition and uniformity of the structure of the steel, reduces the quenching hardness, and deteriorates the mechanical properties. At the same time, it will also reduce the plasticity and toughness of the steel, making the turning dimensions unstable, and the cutters wear quickly. Successive changes in the metallographic structure caused by heating also cause stress, called tissue stress. Overheating is not conducive to heat treatment, which makes the steel brittle and reduces mechanical properties, but can be eliminated by normalizing or annealing after forging.
Cause of damage
The elastic pin coupling is used for the coupling of the elastic pin coupling of the main and slave shafts of the power machine. The circumferentially aligned elastic elements 1 are connected to the master-slave hub bodies 4 and 5 of the coupling, and the helical ring-shaped elastic body of the elastic pin coupling formed by the multi-strand wire strands fixed through the metal splint constitutes the coupling An annular free deformation space is formed between the master-slave hub body, and the coupling master-slave hub body forms an elastic displacement compensation feature through the annular free deformation space in the axial, radial and axial inclination angle directions. It is suitable for shafting connection of various types of power devices (especially with single-layer or double-layer elastic vibration isolation foundation) driven by marine main and auxiliary engines, internal combustion engines, diesel couplings, electric motors and hydraulic motors.
The torsional vibration test is carried out on the ship. From the test results, the torsional vibration characteristics of the coupling are relatively small compared with the allowable value, but the coupling is continuously damaged. In addition to excluding its own quality problems and torsional vibration, what are the general factors? Can it cause damage to the coupling?
1. Principle: The main elastic drum gear coupling of the high elastic coupling is a torsionally loaded rubber component. The rubber component can be designed into a single row or multiple rows, and each rubber component has a variety of standard stiffness to choose from. It can meet the rigidity requirements determined by the torsional vibration calculation to a great extent, the drum-shaped gear coupling. The main purpose of using highly elastic couplings in marine power systems is to transmit power and torque, compensate radial, axial, and angular centering errors, and compensate for oscillations in rotational momentum. Adjust the natural frequency of the system. High elastic pin coupling has the characteristics of light weight, easy installation, large amount of displacement compensation, large damping, strong vibration absorption capacity and frequency modulation ability, etc., which can better protect the main coupling, gear box and shaft system.
2. Reason analysis:
1) The main engine elastic shock absorber sinks, resulting in misalignment of the shaft system and additional torque! This may be great for new ships.
2) Elastic pin coupling rubber drum-shaped gear coupling heat fracture accident; matching problem: only the various devices in the shaft system, such as diesel coupling, high elastic elastic pin coupling, gear box, shaft The other parts and propellers are well designed and complement and support each other, and each improves the design level. The ship designed in this way is a truly high-quality ship.
1. The elastic pin coupling is a nylon rod as the elastic element, and the elastic sleeve pin coupling is rubber or polyurethane as the elastic element, and the effect is different.
2. There is no noise from the elastic sleeve pin, the elastic pin has a certain noise, and the transmitted torque is different.
3. Elastic pin is more commonly used, the transmission torque is relatively large, the effect of the elastic sleeve pin is better, but the elastic sleeve is a wearing part.